1.Introduction
The Federal Decree-Law No. 47 of 2022 on the Taxation of Corporations and Businesses (hereinafter referred to as the “Corporate Tax Law”) was issued by His Highness Sheikh Mohamed bin Zayed Al Nahyan, President of the United Arab Emirates (“UAE President”), on 3 October 2022.
The Corporate Tax Law provides the legislative basis for the introduction and implementation of a Federal Corporate Tax (“Corporate Tax”) in the UAE and is effective for financial years starting on or after 1 June 2023.
The introduction of Corporate Tax is intended to help the UAE achieve its strategic objectives and accelerate its development and transformation. The certainty of a competitive Corporate Tax regime that adheres to international standards, together with the UAE’s extensive network of double tax treaties, will cement the UAE’s position as a leading jurisdiction for business and investment.
Given the position of the UAE as an international business hub and global financial centre, the UAE Corporate Tax regime builds from best practices globally and incorporates principles that are internationally known and accepted. This ensures that the UAE Corporate Tax regime will be readily understood and is clear in its implications
2.What is Corporate Tax?
Corporate Tax is a form of direct tax levied on the net income of corporations and other businesses.
Corporate Tax is sometimes also referred to as “Corporate Income Tax” or “Business Profits Tax” in other jurisdictions.
3.Who is subject to Corporate Tax?
Broadly, Corporate Tax applies to the following “Taxable Persons”:
●UAE companies and other juridical persons that are incorporated or effectively managed and controlled in the UAE;
●Natural persons (individuals) who conduct a Business or Business Activity in the UAE as specified in a Cabinet Decision to be issued in due course; and
●Non-resident juridical persons (foreign legal entities) that have a Permanent Establishment in the UAE (which is explained under Section 8).
Juridical persons established in a UAE Free Zone are also within the scope of Corporate Tax as “Taxable Persons” and will need to comply with the requirements set out in the Corporate Tax Law. However, a Free Zone Person that meets the conditions to be considered a Qualifying Free Zone Person can benefit from a Corporate Tax rate of 0% on their Qualifying Income (the conditions are included in Section 14).
Non-resident persons that do not have a Permanent Establishment in the UAE or that earn UAE sourced income that is not related to their Permanent Establishment may be subject to Withholding Tax (at the rate of 0%). Withholding tax is a form of Corporate Tax collected at source by the payer on behalf of the recipient of the income. Withholding taxes exist in many tax systems and typically apply to the cross-border payment of dividends, interest, royalties and other types of income.
4.Who is exempt from Corporate Tax?
Certain types of businesses or organizations are exempt from Corporate Tax given their importance and contribution to the social fabric and economy of the UAE. These are known as Exempt Persons and include:

In addition to not being subject to Corporate Tax, Government Entities, Government Controlled Entities that are specified in a Cabinet Decision, Extractive Businesses and Non-Extractive Natural Resource Businesses may also be exempted from any registration, filing and other compliance obligations imposed by the Corporate Tax Law, unless they engage in an activity which is within the charge of Corporate Tax.
5.How is a Taxable Person subject to Corporate Tax?
In line with the tax regimes of most countries, the Corporate Tax Law taxes income on both a residence and source basis. The applicable basis of taxation depends on the classification of the Taxable Person.
●A “Non-Resident Person” will be taxed only on income derived from sources within the UAE (i.e. a source basis).
6.Who is a Resident Person?
Companies and other juridical persons that are incorporated or otherwise formed or recognised under the laws of the UAE will automatically be considered a Resident Person for Corporate Tax purposes. This covers juridical persons incorporated in the UAE under either mainland legislation or applicable Free Zone regulations, and would also include juridical persons created by a specific statute (e.g. by a special decree).
Foreign companies and other juridical persons may also be treated as Resident Persons for Corporate Tax purposes where they are effectively managed and controlled in the UAE. This shall be determined with regard to the specific circumstances of the entity and its activities, with a determining factor being where key management and commercial decisions are in substance made.
Natural persons will be subject to Corporate Tax as a “Resident Person” on income from both domestic and foreign sources, but only insofar as such income is derived from a Business or Business Activity conducted by the natural person in the UAE. Any other income earned by a natural person would not be within the scope of Corporate Tax.
7.Who is a Non-Resident Person?
Non-Resident Persons are juridical persons who are not Resident Persons and:
●have a Permanent Establishment in the UAE; or
●derive State Sourced Income.
Non-Resident Persons will be subject to Corporate Tax on Taxable Income that is attributable to their Permanent Establishment (which is explained under Section 8).
Certain UAE sourced income of a Non-Resident Person that is not attributable to a Permanent Establishment in the UAE will be subject to Withholding Tax at the rate of 0%.
8.What is a Permanent Establishment?
The concept of Permanent Establishment is an important principle of international tax law used in corporate tax regimes across the world. The main purpose of the Permanent Establishment concept in the UAE Corporate Tax Law is to determine if and when a foreign person has established sufficient presence in the UAE to warrant the business profits of that foreign person to be subject to Corporate Tax.
The definition of Permanent Establishment in the Corporate Tax Law has been designed on the basis of the definition provided in Article 5 of the OECD Model Tax Convention on Income and Capital and the position adopted by the UAE under the Multilateral Instrument to Implement Tax Treaty Related Measures to Prevent Base Erosion and Profit Shifting. This allows foreign persons to use the relevant Commentary of Article 5 of the OECD Model Tax Convention when assessing whether they have a Permanent Establishment or not in the UAE. This assessment should consider the provisions of any bilateral tax agreement between the country of residence of the Non-Resident Person and the UAE.
9.What is Corporate Tax imposed on?
Corporate Tax is imposed on Taxable Income earned by a Taxable Person in a Tax Period.
Corporate Tax would generally be imposed annually, with the Corporate Tax liability calculated by the Taxable Person on a self-assessment basis. This means that the calculation and payment of Corporate Tax is done through the filing of a Corporate Tax Return with the Federal Tax Authority by the Taxable Person.
The starting point for calculating Taxable Income is the Taxable Person’s accounting income (i.e. net profit or loss before tax) as per their financial statements. The Taxable Person will then need to make certain adjustments to determine their Taxable Income for the relevant Tax Period. For example, adjustments to accounting income may need to be made for income that is exempt from Corporate Tax and for expenditure that is wholly or partially non-deductible for Corporate Tax purposes.
10.What income is exempt?
The Corporate Tax Law also exempts certain types of income from Corporate Tax. This means that a Taxable Persons will not be subject to Corporate Tax on such income and cannot claim a deduction for any related expenditure. Taxable Persons who earn exempt income will remain subject to Corporate Tax on their Taxable Income.
The main purpose of certain income being exempt from Corporate Tax is to prevent double taxation on certain types of income. Specifically, dividends and capital gains earned from domestic and foreign shareholdings will generally be exempt from Corporate Tax. Furthermore, a Resident Person can elect, subject to certain conditions, to not take into account income from a foreign Permanent Establishment for UAE Corporate Tax purposes.
11.What expenses are deductible?
In principle, all legitimate business expenses incurred wholly and exclusively for the purposes of deriving Taxable Income will be deductible, although the timing of the deduction may vary for different types of expenses and the accounting method applied. For capital assets, expenditure would generally be recognized by way of depreciation or amortization deductions over the economic life of the asset or benefit.
Expenditure that has a dual purpose, such as expenses incurred for both personal and business purposes, will need to be apportioned with the relevant portion of the expenditure treated as deductible if incurred wholly and exclusively for the purpose of the taxable person’s business.
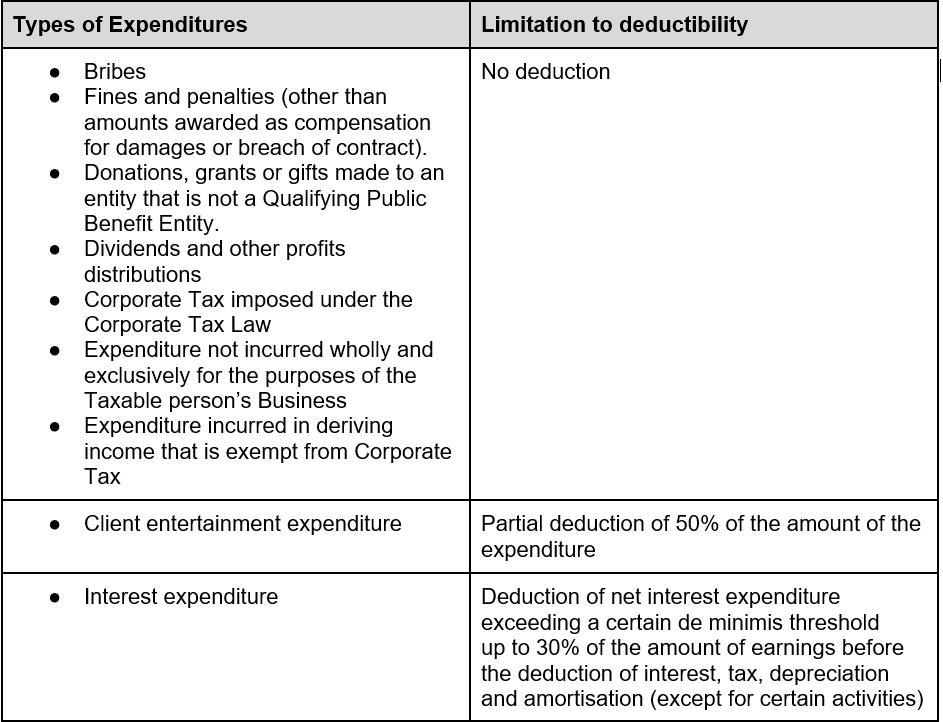
Certain expenses which are deductible under general accounting rules may not be fully deductible for Corporate Tax purposes. These will need to be added back to the Accounting Income for the purposes of determining the Taxable Income. Examples of expenditure that is or may not be deductible (partially or in full) include:
Need Help!
KBA experts will help you
Just contact us any time
